In the rapidly transforming world of digital innovation, search engines are no longer limited to retrieving exact-match keywords.— they’re transforming into conversational, context-aware tools powered by artificial intelligence (AI). Enter Generative Engine Optimization (GEO), the next big thing in digital marketing that bridges the gap between traditional SEO practices and AI-driven search results. Whether you are a content creator, marketer, or company owner, learning how to optimize for generative engines is critical to being competitive in tomorrow’s search economy.
This tutorial will walk you through all you need to know about Generative Engine Optimization, from the fundamentals to advanced methods, so you can remain ahead in the age of AI-powered search.
What is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)?
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is the process of customizing content, keywords, and website architecture to match how AI-driven generative search engines, such as those powered by large language models (LLMs), extract and rank information. Unlike traditional SEO, which focusses on optimizing for search engines like as Google or Bing, GEO prioritizes AI-powered engines that employ generative AI to deliver conversational and contextually relevant answers to user questions. These engines don’t just display a list of links for users to explore—they generate synthesized, human-like answers based on an understanding of the query. GEO is about ensuring your content is part of the AI’s response, whether it’s through semantic SEO strategies, natural language search optimization, or prompt optimization for search.
Why is Generative Engine Optimization Important?
As AI transforms online search and interaction, GEO is increasingly important in digital marketing strategy. Here’s why this matters:
The Rise of Generative AI in Search
AI Tools like as OpenAI’s ChatGPT, Google Gemini, and Bing Chat are changing the way people engage with search engines. Rather than just listing webpages, generative engines offer direct, conversational responses. If your content is not optimized to appear in these responses, you risk losing visibility.
Search Intent is Shifting
Modern consumers demand rapid gratification. Generative engines employ natural language processing (NLP) and contextual keyword research to better grasp user intent, making keyword-stuffing tactics less effective.
Future-Proofing Your Content
AI-powered search ranking variables, such as context signals and topical authority, are becoming increasingly important. GEO assists content providers in adapting to these developing requirements, assuring long-term relevance.
Enhanced User Experience
Generative AI personalizes search results and provides responses in a conversational tone. Optimizing for this form of search increases the probability of your content getting listed, resulting in more engagement and conversions.
How Is Generative Engine Optimization Different from Traditional SEO?
Aspect | Traditional SEO | Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) | |
Focus | Keywords and backlinks | Context, semantics, and AI-generated answers | |
Search Engines | Google, Bing, Yahoo | AI tools like ChatGPT, Google Gemini | |
Content Format | Optimized for search engine crawlers | Designed for conversational, NLP-driven engines | |
Ranking Factors | Keywords, metadata, backlinks | User intent, context signals, topical authority | |
Output | List of links | Direct conversational answers | |
It’s clear that GEO goes beyond traditional SEO tactics, requiring a deeper understanding of search engine context signals and AI-driven content discovery.
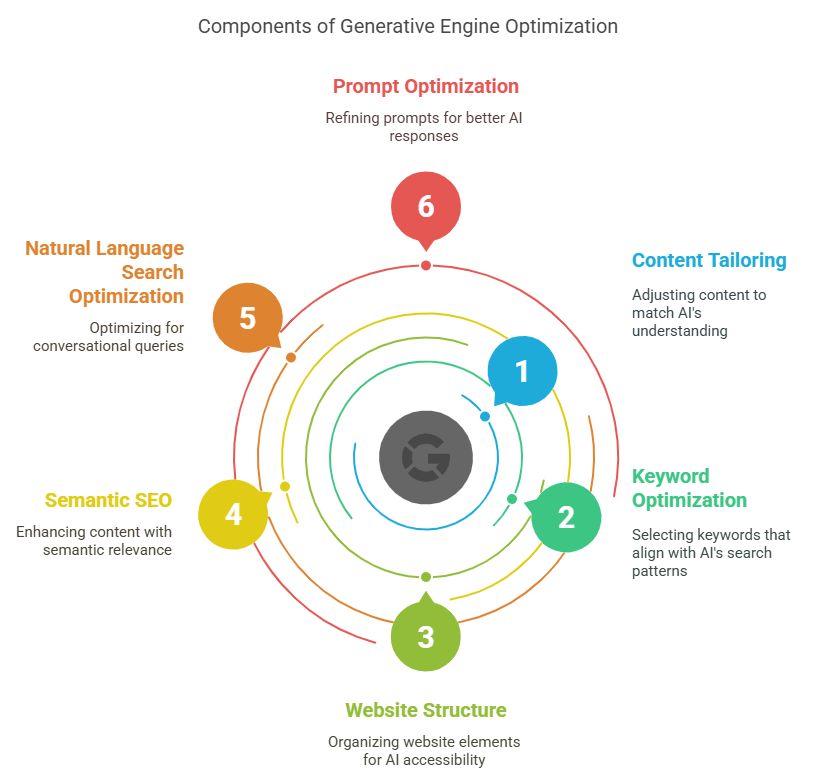
Key Components of Generative Engine Optimization
To succeed with GEO, you need to focus on several core components that cater to AI-driven search engines. Here’s a breakdown of the most important aspects:
Semantic SEO Strategies
Generative engines rely heavily on understanding the meaning behind words rather than just matching keywords. Semantic SEO involves creating content that addresses broader topics and subtopics, focusing on the relationships between terms.
How to implement:
- Use contextual keyword research to identify related terms and concepts.
- Use keyword clustering for AI to organize related terms into groups.
- Write in-depth content that answers multiple related questions.
Natural Language Search Optimization
Generative engines are designed to interpret human-like queries. Optimizing for natural language search guarantees that your content follows conversational trends:
- Use long-tail keywords that mimic how people speak.
- Incorporate People Also Ask keywords for GEO into your content.
- Answer questions in a conversational, easy-to-digest tone.
Prompt Optimization for Search
In generative search, users often phrase queries like prompts. This opens a new avenue for optimizing your content to align with these queries.
- Anticipate user prompts and create content that directly addresses them.
- Experiment with search intent analysis to predict the type of questions users may ask.
AI Content Ranking Factors
Generative engines assess content in a different way than typical search engines. Key factors include:
- Topical authority in AI search: Demonstrate expertise in your niche by covering a topic comprehensively.
- AI content ranking factors: Focus on readability, relevance, and user engagement metrics.
Context and Intent Signals
AI engines analyze search engine context signals, such as the user’s intent, query history, and context. You can optimize for this by:
- Striving for long-tail keyword optimization to address specific intents.
- Structuring content to provide clear, actionable value.
- Using AI-driven content discovery tools to identify trending topics in your niche.
Conversational Search Optimization
Generative engines prioritize conversational responses. This means your content must be:
- Engaging: Write in a natural, conversational tone.
- Interactive: Use FAQs, bulleted lists, and summaries to mimic conversational flow.
- Relevant: Address user pain points and offer solutions.
Step-by-Step Guide to Implement Generative Engine Optimization
Here’s an overview of the most crucial aspects:
Step 1: Conduct Contextual Keyword Research
- Use tools like SEMrush, Ahrefs, or AI-driven platforms to identify semantic keywords and People Also Ask keywords for GEO.
- Group keywords into clusters based on topic relevance.
Step 2: Create AI-Friendly Content
- Write long-form content that answers multiple user queries.
- Incorporate search intent analysis to ensure content aligns with what users are searching for.
- Structure content with subheadings, bullet points, and summaries to enhance readability.
Step 3: Focus on Topical Authority
- Publish consistent, high-quality content that covers topics deeply.
- Link internally to related content on your site to improve AI-powered search ranking.
Step 4: Optimize for Conversational AI
- Rewrite content to match natural language search optimization.
- Use AI tools like ChatGPT or Jasper to test how generative engines interpret your content.
Step 5: Track Performance and Adjust
- Monitor traffic, engagement, and rankings using tools like Google Analytics and AI-specific dashboards.
- Regularly update content to reflect new AI content ranking factors.
Final Thoughts: Embracing the Future of Search
Generative Engine Optimization is more than simply a fad; it is a must-have for businesses and content providers hoping to succeed in the age of AI-powered search. By focusing on semantic SEO methods, natural language search optimization, and AI-friendly content, you can keep your website accessible and relevant in this new search paradigm. The future of search is conversational, context-driven, and powered by generative AI.
Are you prepared to optimize your content for the next chapter in digital marketing?
With this thorough guide, you will have the information and tactics you need to grasp Generative Engine Optimization—the key to staying competitive in today’s AI-driven world.
